Our Blog
09.30.2019
Physical Therapy is the #1 Treatment for Torticollis
Torticollis is a relatively common condition that babies can develop in utero or after birth. While there are alternative treatment options that some families choose to participate in, physical therapy is the preferred treatment intervention for torticollis. 7/10 of the top 10 children’s hospitals in the United States specifically recommend physical therapy for the treatment

07.02.2019
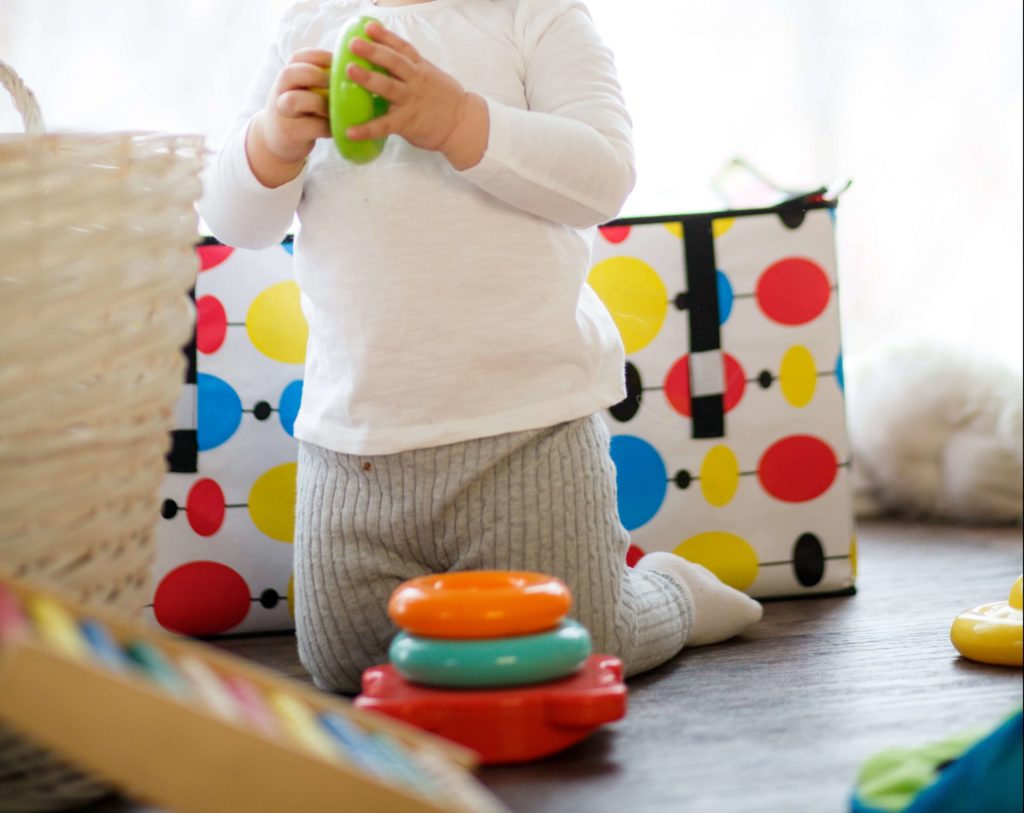
Gross Motor Milestone Series: Kneeling
Kneeling is a critical gross motor milestone that kids use in many ways. It is a position that can be used for playing or as a transitional movement to get from one position to another, such as moving from the floor to standing. There are also a few different variations of kneeling, including short kneeling,

05.01.2019
Developmental Communication Milestone Series: 18 Months
What does communication at 18 months of age look like? Toddlers are understanding many more words and phrases than they are able to say. They are able to understand words used to describe what is happening now, as well as words to describe what will happen next. Toddlers at this age are also able to

11.05.2019
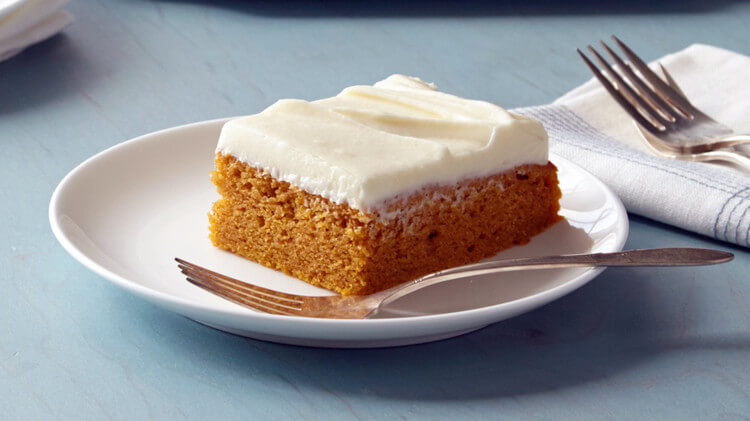
Pumpkin Sheet Cake Recipe
This pumpkin sheet cake recipe is easy to make and delicious. Makes 36 Servings For the Cake: 2 Cups Sugar 1 Cup Vegetable Oil 2 Cups Solid Pack Pumpkin 4 Extra Large Eggs 2 Cups All Purpose Flour 2 Teaspoons Baking Powder 1 Teaspoon Baking Soda ½ Teaspoon Salt 1 Teaspoon Ground Ginger 2 ½

09.03.2019
Developmental Communication Milestone Series: 24 Months
Communication at 24 months includes following directions and understanding words. They understand simple questions and provide simple one or two-word answers along with nodding head for yes or no. Toddlers are able to understand explanations of events that are taking place and understand when they are told something cannot happen until later in the day,

06.05.2019
24/7 Postural Care: What Is It and How Could It Help You?
Daytime and nighttime positioning are an integral part of daily life. 24/7 postural care can make a huge difference. Easily overlooked and often misunderstood, positioning is something most individuals take for granted. For several individuals, however, body changes due to positioning and gravity are more immediate and more debilitating. In addition, people who have limited